Eloctate (efmoroctocog alfa) for hemophilia
What is Eloctate for hemophilia?
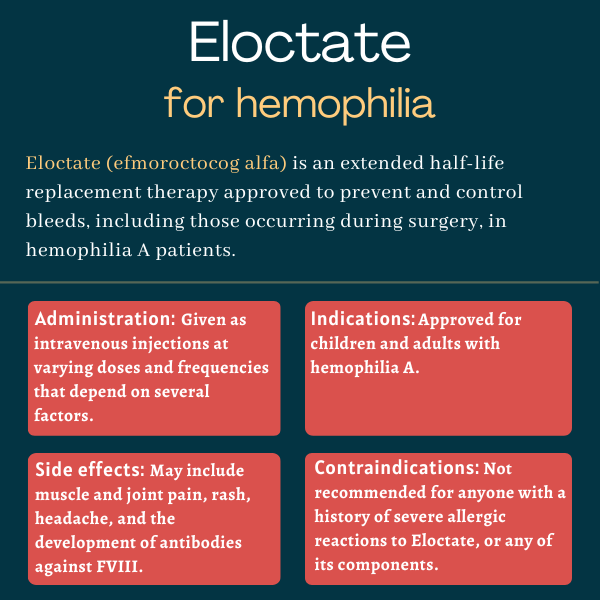
Eloctate (efmoroctocog alfa) is an extended half-life therapy that’s approved to prevent and treat bleeds, including those occurring during surgery, in adults and children with hemophilia A.
Its design allows it to last for a longer time in the body, thus requiring fewer doses.
The therapy, which is administered via an intravenous or into-the-vein injection, is marketed by Sanofi in the U.S., Canada, Japan, and other countries. Sobi markets the therapy under the brand name Elocta in the European Union, and in Iceland, Kuwait, Liechtenstein, Norway, Saudi Arabia, Switzerland, and the U.K.
Eloctate was originally developed by Biogen and then by Bioverativ Therapeutics, which was acquired by Sanofi in 2018.
Therapy snapshot
| Brand name: | Eloctate |
| Chemical name: | Efmoroctocog alfa |
| Usage: | Prevention and treatment of bleeds, including those occurring during surgery, in hemophilia A patients |
| Administration: | Intravenous injection |
How does Eloctate work?
Hemophilia A is caused by the lack or malfunction of a clotting protein called factor VIII (FVIII) that results in prolonged and excessive bleeding.
A replacement therapy, Eloctate contains a recombinant, or man-made, version of FVIII that can be administered to individuals with hemophilia A to restore blood clotting and prevent excessive bleeding.
Eloctate is an extended half-life therapy, a class of replacement therapies in which the FVIII protein is modified so that it lasts longer in the body to allow for less frequent dosing.
Specifically, Eloctate contains a version of FVIII that’s attached to a piece of an antibody called a fragment crystallizable (Fc) region. This type of modification, called an Fc fusion, helps ensure FVIII remains in circulation and is not degraded as fast as it normally would be.
Eloctate has a half life that’s 1.5 times longer than Advate (octocog alfa), another approved replacement therapy for hemophilia A marketed by Takeda. Half-life refers to the amount of time it takes for the levels of a molecule to drop by half in the bloodstream.
Who can take Eloctate?
Eloctate was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in June 2014 for adults and children with hemophilia A. It can be used as:
- an on-demand treatment to control active bleeds
- a perioperative treatment, meaning one given around the time of surgery, to reduce bleeding during and after medical or dental procedures
- as a routine prophylactic or preventive treatment to lower the risk of bleeds.
The FDA decision made Eloctate the first recombinant FVIII product with proven prolonged circulation to be approved for hemophilia A in the U.S. That same year, Eloctate was approved by Health Canada for the control and prevention of bleeding episodes and routine prophylaxis in hemophilia A patients ages 12 and older in that country.
The European Commission approved the therapy — under the brand name Elocta — in November 2015 as a preventive and on-demand treatment for bleeds, inducing those happening during surgery, in people with hemophilia A of all ages.
Who should not take Eloctate?
Eloctate is contraindicated, or not recommended, for anyone who experienced a severe allergic reaction to the medication or to any of its components, including sucrose, sodium chloride, L-histidine, calcium chloride, and polysorbate.
The therapy also is not indicated for treating von Willebrand disease, another inherited bleeding disorder.
How is Eloctate administered?
Eloctate is given as an injection into the bloodstream, and may be self-administered after appropriate training by a healthcare provider.
The therapy is available in single-use vials containing varying amounts of FVIII, expressed in international units (IUs). Vials are available in 10 different strengths, which are color-coded:
- Yellow contains 250 IUs.
- Red is a 500 IU strength.
- Garnet contains 750 IUs.
- Green contains 1,000 IUs.
- Dark green is a 1,500 IU strength.
- Royal blue is a 2,000 IU strength.
- Mist grey contains 3,000 IUs.
- Orange is a 4,000 IU strength.
- Mist brown contains 5,000 IUs.
- Purple contains 6,000 IUs.
The therapy is supplied as a white to off-white powder, which must reconstituted, or diluted, using a pre-filled syringe containing 3 mL of sterile water. Eloctate should be administered within three hours of reconstitution.
The treatment dosage and duration depend on the location and extent of the bleed, the severity of FVIII deficiency, and the patient’s clinical condition.
When used on-demand to control bleeding, or as part of surgical management, the dose of Eloctate is also calculated based on the severity of the bleed or the complexity of the surgery.
The recommended dose for on-demand treatment of minor and moderate bleeding episodes, such as superficial muscle and soft tissue bleeds, is 20-30 IU per kilogram of body weight (IU/kg). In these cases, Eloctate should be given every 24-48 hours (or every 12-24 hours in children younger than 6) to maintain FVIII activity levels at 40-60 IU/dL until the bleed is resolved.
For on-demand treatment of major bleeding episodes, such as life-threatening bleeds or those occurring in the brain or gastrointestinal tract, the recommended dose is 40-50 IU/kg. In such cases, Eloctate should be given every 12-24 hours (or every 8-24 hours in children younger than 6) to maintain FVIII activity levels at 80-100 IU/dL until the bleed is resolved (for approximately 7-10 days).
For minor surgeries, such as an uncomplicated tooth extraction, the recommended dose is 25-40 IU/kg, given every 24 hours (or every 12-24 hours in children younger than 6) to maintain FVIII activity levels at 50-80 IU/dL for at least one day until healing is achieved.
For major surgeries, such as joint replacement surgery or procedures involving the brain, it’s recommended that patients be given a dose of 40-60 IU/kg before surgery. This should be followed by a repeat dose of 40-50 IU/kg after 8-24 hours (6-24 hours in children younger than 6), and then every 24 hours to maintain FVIII activity levels at 80-120 IU/dL. Dosing should be maintained until adequate wound healing is achieved, and followed for at least seven days to maintain FVIII activity levels within the target range of 80-120 IU/dL.
For routine prophylaxis, the recommended starting dose is 50 IU/kg every four days for patients ages 6 and older, or 50 IU/kg twice weekly for children younger than 6. Based on how the patient responds to treatment, dosing regimens may then be adjusted to anywhere from 25 to 65 IU/kg, given every three, four, or five days. For children younger than 6, more frequent or higher doses, up to 80 IU/kg, may be required.
Patients may self-administer Eloctate after receiving proper training from a healthcare professional, who may oversee the first time they administer themselves a dose. Individuals who have not been trained should never attempt to self-infuse the therapy.
Eloctate in clinical trials
The therapy’s approvals were supported by data from two Phase 3 trials that enrolled previously-treated males with severe hemophilia A. The A-LONG trial (NCT01181128), completed in 2012, enrolled 165 adults and adolescents, ages 12 to 65, while the Kids A-LONG study (NCT01458106), which wrapped up in 2013, enrolled 71 boys younger than 12.
In both studies, most patients were given prophylactic treatment with Eloctate. The therapy also was used to control bleeds and manage surgical bleeding during the trials. A few participants in the adult study did not receive preventive treatment and instead received Eloctate only as needed for bleeds or surgeries.
The results from both studies showed that, when bleeding episodes occurred, a single injection of Eloctate was usually sufficient to control bleeding. More than 90% of bleeds in both studies — 97.7% in A-LONG and 93% in Kids A-LONG — were controlled with one or two injections.
When used as an on-demand treatment, the response to the first injection was rated as “excellent” or “good” — meaning that treatment led to clear improvements in bleeding and pain control for the patient — in most cases for adults and adolescents (78.1%), as well as for children (92.6%).
In all major and minor surgeries that occurred during the trials, the efficacy of Eloctate was also rated as “excellent” or “good,” meaning that blood loss did not cause any surgical complications.
Results from the trials also showed that preventive treatment with Eloctate was generally effective at reducing bleed rates for patients. The median annualized bleed rate was 1.6 bleeds per year for adult and adolescent patients given Eloctate prophylaxis, and two bleeds per year for children. Compared with adults given on-demand treatment with Elocate only, this represented a 92% reduction in bleed rates.
ASPIRE extension study
Patients who completed A-LONG or Kids A-LONG had the option to enroll in a long-term extension study called ASPIRE (NCT01454739), which also supported the approval of Eloctate.
The extension study enrolled a total of 240 patients, including 150 who participated in A-LONG, 61 from Kids A-LONG, and 29 who participated in two smaller trials assessing the safety and pharmacological properties of Eloctate.
Results showed that long-term prophylactic treatment with Eloctate effectively kept bleed rates low: Adults and adolescents had a median annualized bleed rate of 0.7 bleeds per year, while children had 1.6 two bleeds per year.
Similar to previous studies, one or two injections of Eloctate were sufficient to control more than 93% of bleeds in the extension study. The efficacy of Eloctate at controlling surgical bleeding was also rated as “excellent” or “good” in all surgeries.
Common side effects of Eloctate
In previously-treated hemophilia A patients, the most common side effects of Eloctate observed in clinical trials were:
- joint pain (arthralgia)
- muscle pain (myalgia)
- headache
- rash
- general feeling of discomfort (malaise).
For previously-untreated patients, common side effects of Eloctate included:
- development of antibodies against FVIII (inhibitors)
- device-related blood clotting complications (thrombosis)
- rash.
Allergic reactions
Allergic reactions to Eloctate have been reported. Signs of an allergic reaction, which may progress to a serious anaphylactic reaction, may include swelling, chest tightness, shortness of breath, wheezing, itching, and hives.
If an allergic reaction occurs, Eloctate should be immediately discontinued, and appropriate care should be given to manage the reaction.
Development of inhibitors
Some patients treated with Eloctate have developed inhibitors — antibodies made by the immune system that target the clotting factor in Eloctate, potentially rendering the treatment ineffective. Patients on Eloctate should be closely monitored for the presence of inhibitors, especially if they don’t respond to the treatment as well as expected.
Cardiovascular events
Because cardiovascular events often involve abnormal blood clotting, hemophilia patients may be at a lower risk of experiencing such events compared with individuals from the general population.
However, once blood clotting has been normalized by treatment with Eloctate, hemophilia patients with cardiovascular risk factors may be at a similar risk of developing cardiovascular events as non-hemophilic patients.
Catheter-related complications
In some patients requiring frequent infusions, a central venous catheter, or a tube implanted in a large vein, may be placed for easy vein access. In these cases, patients may be at risk of experiencing a series of catheter-related complications, including local infections, bacteremia (bacteria in the bloodstream), and thrombosis (blood clots that clog blood vessels) at the catheter site.
Use in pregnancy and breastfeeding
Eloctate has not been rigorously studied in people who are pregnant or breastfeeding. Animal studies have indicated that small amounts of the medication can cross the placenta to a developing fetus during pregnancy, but the clinical relevance of these data for human patients isn’t clear. Thus, it’s not known whether Eloctate may potentially cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman.
It’s also not known if Eloctate can pass into breastmilk, affect milk production, or impact the nursing infant. In these situations, patients and their care teams should weigh the potential benefits and risks of continuing or stopping treatment with Eloctate.
Hemophilia News Today is strictly a news and information website about the disease. It does not provide medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. This content is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this website.
Recent Posts
- Battling self-doubt as a woman with bleeding disorders
- Extended hemophilia half-life products aid care, but raise costs
- I’m encouraged to see my son take initiative in solving a problem
- Why asking for and accepting help is important for parents
- What I’ve learned about obesity, joint pain, and hemophilia bleeds
Related articles

 Fact-checked by
Fact-checked by